Cloud Shared Responsibility Model
- Description
- Curriculum
- Reviews
– Why Cloud?
– Introduction to Cloud Computing
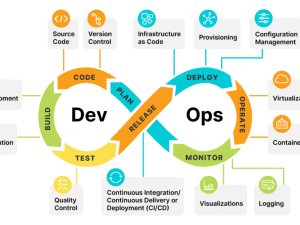
– Why DevOps on Cloud?
– Types: Deployment Model and Service Model
There are 4 types of cloud deployment models Public cloud, private cloud, Hybrid cloud, and community cloud.
Public Cloud –
Public Cloud, is a type of hosting in which cloud services are delivered over a network for public use. Is made available to the general public over the internet and owned by a cloud provider. Example: AWS, Microsoft Azure, IBM, Oracle…They are environments typically created from IT environment not owned by the end user.
- Customers do not have any control over the location of the infrastructure.
- The cost is shared by all users and is either free or in the form of a license policy like pay per user.
- Public clouds are great for organizations that require managing the host application and the various applications users use.
Private Cloud –
A private Cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is solely used by one organization. They are environments solely dedicated to a single end user or group, where the environment usually runs behind that user or group’s firewall. All clouds become private clouds when the underlying IT infrastructure is dedicated to a single customer with completely isolated access. Is exclusively operated by a single organization. It can be managed by the organization or a third party and may exist on-premise or off-premise. Example: VMware, AWS
- It gives organizations greater control over security and data safeguarded by a firewall and managed internally.
- It can be hosted internally or externally.
- Private clouds are great for organizations that have high-security demands, high management demands, and uptime requirements.
Hybrid Cloud –
Hybrid Cloud uses both private and public clouds but can remain separate entities. Hybrid Cloud is a seemingly single IT environment created from multiple environments connected through local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), virtual private networks (VPNs), and/or APIs. They are managed private cloud where customers create and use a private cloud that’s deployed, configured, and managed by a third-party vendor and dedicated cloud. It consists the functionalities of both public and private cloud. Examples: Federal agencies opt for private clouds when sensitive information is involved. Also they use the public cloud to share datasets with general public or other government departments The characteristics of hybrid clouds are complex and the requirements can differ, depending on whom you ask. For example, a hybrid cloud may need to include:
- At least one private cloud and at least one public cloud
- Two or more private clouds
- Two or more public clouds
- A bare-metal or virtual environment connected to at least one public cloud or private cloud
- Resources are managed and can be provided either internally or by external providers.
- A hybrid cloud is great for scalability, flexibility, and security.
- An example of this is an organization that can use the public cloud to interact with customers while keeping their data secured through a private cloud.
Community Cloud
It is an infrastructure that is mutually shared between organizations that belong to a particular community.
- The community members generally share similar privacy, performance, and security concerns.
- An example of this is a community cloud at banks, the government in a country, or trading firms.
- A community cloud can be managed and hosted internally or by a third-party provider.
- A community cloud is good for organizations that work on joint ventures that need centralized cloud computing ability for managing, building, and executing their projects.
-
1What is Cloud Computing?Text lesson
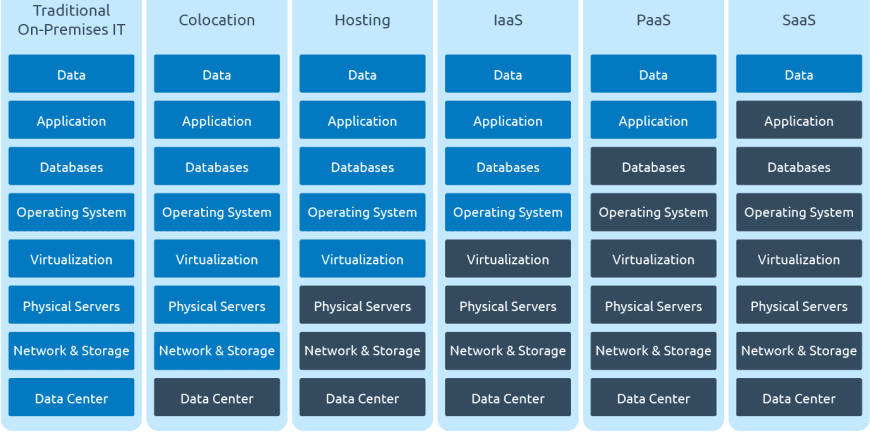
Cloud computing is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the internet. These services are divided into three main categories or types of cloud computing: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
-
2Cloud Computing Deployment ModelsText lesson
Private Cloud Services
Public Cloud Services
A Hybrid Cloud
-
3Cloud Computing Service ModelsText lesson
Cloud Computing Service Models
Characteristics of Cloud Computing model – PaaS
PaaS provides a web-based development environment.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing model – SaaS
SaaS enables the software available over the Internet.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing model – IaaS
-
4Cloud Computing Characteristics and its relevanceText lesson
Recent Posts
- Google Cloud Platform’s Latest Innovations: Transforming the Future of AI and Cloud Computing
- Exploring Azure’s Cutting-Edge Services in 2025: A Step Towards a Smarter Future
- What Businesses Need to Know About Quantum Computing and Big Data
- The Future of Edge AI and Its Impact on Cloud SaaS Solutions
- AI, Big Data, and Cloud SaaS: A Triple Threat for Business Growth